#3: The Ultimate Forex Trading Webinar for Beginners
Lesson 3
Welcome to the...
Ultimate Forex Trading Webinar for Beginners
This is for you if you are new to Forex trading.
You have less than a year of experience.
And you want to learn more about the Forex market…
Then this course will benefit you greatly.
What is Forex Trading
The word Forex refers to “Foreign Exchange."
What you are doing is trading one currency for another.
Who trades Forex and why
There are numerous market participants who trade Forex.
For example:
- Central banks
- Banks
- Corporations
- Retail traders
Central bank
Central banks want to make their economy more competitive by devaluing their currency.
This makes their currency cheaper and exports will be more attractive.
Banks
Banks could be a market maker.
They are making a market in the FX market or they may be trying to hedge their portfolio.
Corporations
Corporations need to buy raw materials.
So, they would need to be involved in the Foreign Exchange.
For example, I am Toyota and I need to buy raw materials for the tires.
And let’s say that the tires will be coming from India.
What I’ll do is that I will need to sell some Japanese Yen (JPY) and buy Indian Rupees (INR).
I’ll take these Indian Rupees and go to companies in India to exchange for the raw materials for the tires.
Retail traders
For retail traders…
They could be trading the Forex market to speculate or to generate better returns compared to putting their money in the bank.
These are the few groups of traders who trade the Forex market!
The Forex market ecosystem
As you can see over here:
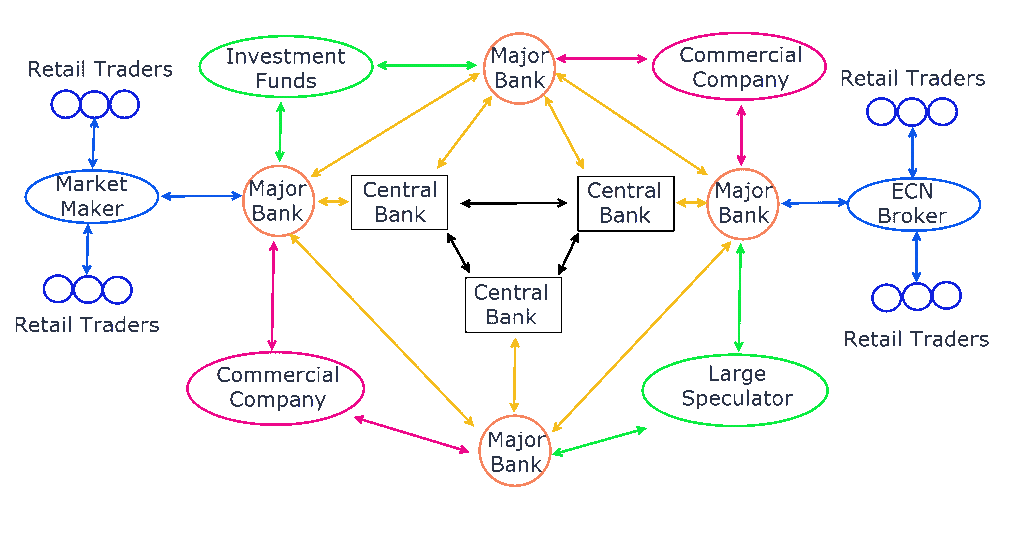
This is how the network of the Forex market looks like.
In the center, they are Central Banks and then Major Banks.
Then, you have the Investment Funds and Commercial Company trading with the banks.
Finally, retail traders like you and me who trades in the market as well.
The Forex market hierarchy
This is the hierarchy of the Forex market:
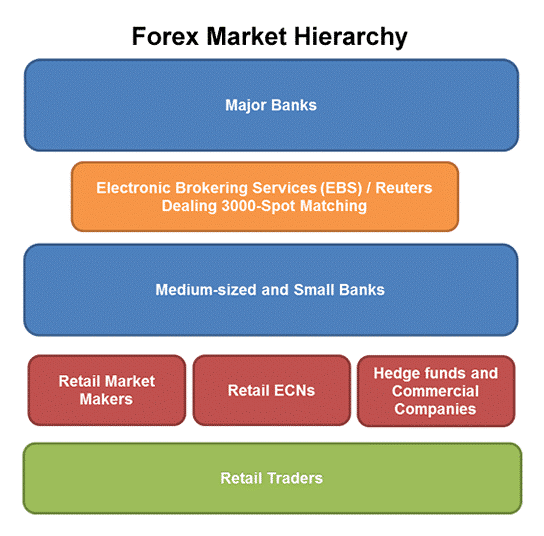
You can see that Major Banks are at the top of the food chain.
Followed by Medium-sized or small banks, retail market makers, and finally Retail traders at the bottom.
Source: Babypips
Moving on...
What are the advantages of Forex Trading
There are numerous advantages of Forex trading:
- High liquidity
- Low barrier to entry
- Better risk management (Low transaction costs)
- Trade anytime you want
Let me explain…
High liquidity
Unlike stocks, especially penny or small-cap stocks…
There is no liquidity and you have to pay a very wide bid/ask spread.
For the Forex market, it typically has high liquidity.
This means that you can get in and out of your trades relatively easy, without paying a huge premium or spread.
Low barrier to entry
This means that anyone can open a Forex trading account.
You don’t need to be a high net worth individual and etc.
Better risk management
Certain Forex brokers allow you to trade in Nano Lots.
This in return allows you to better manage your risk.
One of the biggest problems of most stock traders face is, for example, you have a small capital of $500…
And if you want to apply proper risk management on stocks, it can be difficult.
Because let’s say you want to risk 1% of your account ($5).
If you pay your transactions costs, it’s going to be more than $5 for stocks!
Depending on the broker, one round trip charge could be $10.
So, it’s difficult to apply proper risk management on stocks especially with a small account.
But for Forex, it’s possible because you can trade Nano Lots.
This allows you to risk $5 on a trade.
Most forex brokers allow you to only pay for the spread and no commissions.
Trade anytime you want
The Forex market is open for 24/5 from Monday to Friday.
When you wake up, the market is open.
When you sleep, the market is still open.
Quick Recap
- Forex trading is the exchange of currencies
- Traded by banks, corporations and retail traders
- Advantages: High liquidity, low barrier to entry, better risk management, trade anytime, low transaction cost
Now, what are some of the different currency pairs in the market?
The different currency pairs
There are three currency pairs that you should be aware of:
- Major Pairs
- Crosses
- Exotic Pairs
Let me explain…
The major currency pairs (USD)
The major currency pairs are typically pairs that are the most liquid and has a dollar element to it:
- EUR/USD (Euro Dollar)
- GBP/USD (Pound Dollar)
- USD/CHF (Dollar Swissy)
- USD/JPY (Dollar Yen)
- AUD/USD (Aussie Dollar)
- NZD/USD (Kiwi Dollar)
- USD/CAD (Dollar Loonie)
Notice that they all have the USD element in all of these currency pairs.
These 7 currency pairs are the most liquid and most popular pairs.
If you look at this:
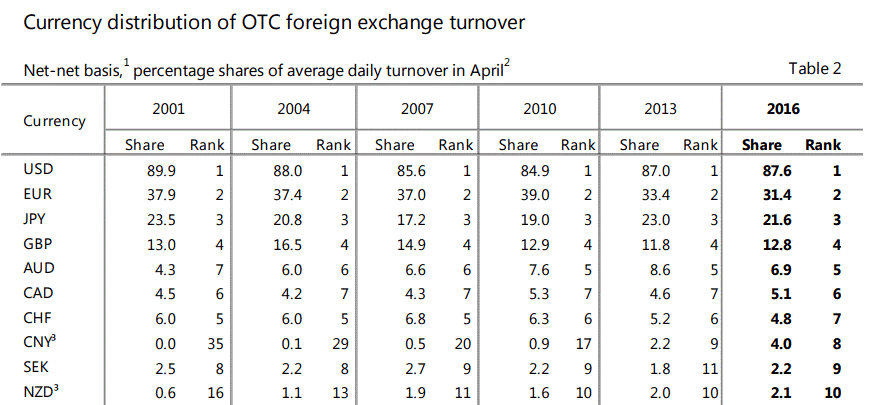
In 2016, the most actively traded pair is the USD.
Followed by EUR, GBP, etcetera…
The cross-currency pairs (non-USD)
These pairs don’t have the USD element to it:
Euro Crosses:
- EUR/CHF
- EUR/GBP
- EUR/AUD
Yen Crosses:
- EUR/JPY
- GBP/JPY
- AUD/JPY
Pound Crosses:
- GBP/AUD
- GBP/NZD
- GBP/CAD
Now, what about Exotic pairs?
The exotic currency pairs
These pairs are usually thinly traded and have a wider bid/ask spread.
The swings in these markets can be more volatile as well.
Some of these examples are:
- USD/ZAR
- USD/MXN
- USD/TBH
- USD/INR
- USD/TRY
Moving on, let’s talk about…
The different Forex trading sessions
Unlike the stock markets where there is only one session…
The Forex market has three different sessions:
- New York Session
- London Session
- Asian Session
And they all open at different times of the day.
Even worse, these times of the day are often not fixed because it depends where you are in the world.
If you are in Asia, your time zone is different compared to someone in New York!
So, I am going to go with a general example and assume that you are from the US.
For the summer period (April – October):
- Asian session starts from 6 pm to 3 pm EDT
- London session starts from 3 pm to 12 am EDT
- New York session starts from 8 am to 5 pm EDT
What if you are not in the US, maybe you are in London, Singapore, or Malaysia…
How would you translate this to your local time zone?
Just go down to google and search for “Forex trading session hours.”
I am sure there would multiple results that would tell you your currency Forex session in your local time zone.
During the winter period (October – April)
- Asian session starts from 6 pm to 3 pm EST
- London session starts from 3 pm to 12 am EST
- New York session starts from 8 am to 5 pm EST
Next…
Which is the best session to trade Forex
This applies almost to any markets that the best time to trade is when there is volatility in the markets.
Only when there is volatility can you make a profit!
When the market does not move…
You’re not going to make money at all.
You cannot squeeze blood out of a rock.
So, you need to be trading when there is most volatility in the markets.
The most volatile session is the London session.
To be precise, the most volatile period is the London and New York overlap session.
As you can see here:
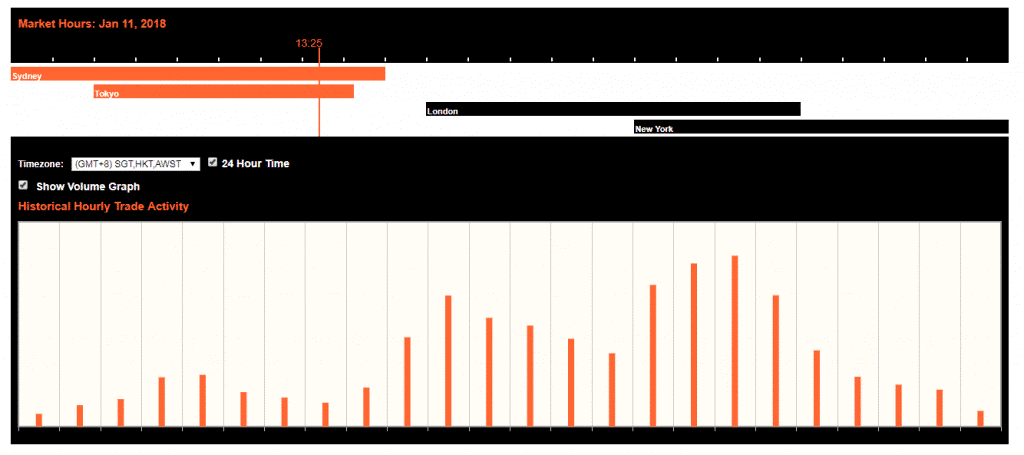
Source: Oanda
You can see that when the London session starts.
Volatility has picked up.
Historically, the market is most volatile during the London and New York overlap as you can see in the example.
Now…
When are the best days to trade Forex?
Best days to trade Forex
The concept is still the same, you want to be trading Forex when the markets tend to move a lot on certain days.
Which days does the Forex market tend to move the most?
Tuesday to Thursday generally is where the Forex market moves the most:
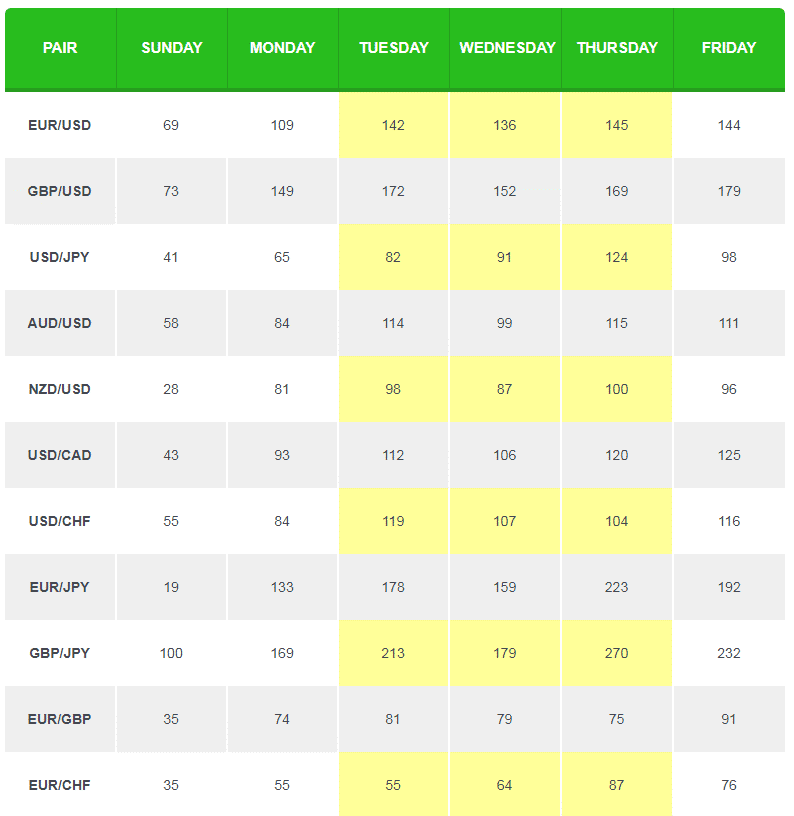
Source: Babypips
You can see the movement of the currency pairs of the week on average.
For example…
EUR/USD tends to move around 142 pips on Tuesday.
On Wednesday, it tends to move around 136 pips.
And on Thursday, 145 pips on average.
You can see that Tuesday to Thursday tends to be when the Forex markets move the most.
If you ask me, those days are the best days of the week to trade Forex.
Next…
Common trading terminologies
Let’s talk about some common Forex trading terminologies.
This may be slightly different from stocks.
But generally, the concepts can be applied as well.
We’ll talk about:
- Long/Short
- Leverage & Margin
- Pip
- Bid/Ask
- Spread
Now let me explain…
Long/Short
To put it simply, when you say that “I’m long EUR/USD.”
It means that you are referring to the trade direction.
You’re bullish on EUR/USD, and you want EUR/USD to go up because that’s where you’ll make a profit.
If you are short, it means that you want the market to go down so you can make a profit.
This means that you have a bearish bias.
Leverage & Margin
Leverage refers to how much more you can trade relative to your account size.
For example, let’s say you have a $10,000 trading account.
And you are using a leverage of 1:10.
This means you can control 10x more than your initial capital.
This means that your broker lets you trade up to $100,000 worth of currency.
This is what leverage means.
The margin is another way of looking at leverage.
If you take 100/10 (leverage), your margin requirement is 10%.
So, if you want to trade $100,000 worth of currency, you’re only required to put 10% of your margin which is $10,000.
One thing to point out is that leverage is a double-edged sword.
You can make more in trading, but at the same time, you can lose more.
For example, let’s say that you have a $10,000 and you are using a 1:10 leverage of $100,000.
And let’s say you want to buy shares of AAPL which is currently valued at $100 per share.
When AAPL shares rise to $110 and you are trading without leverage, you have made a gain of $1,000.
But if you are using leverage, you have made a gain of $10,000.
If you put it into perspective in percentage terms…
What happens is that without leverage, you have made a return of 10%
But with leverage, you have made a 100% return of your money.
This might look good and sounds really awesome!
But I want you to take note that what happens if the shares of AAPL drops by 10%?
From $100 down to $90 per share.
Without leverage, you would lose $1,000
But if you are trading with leverage, you would lose $10,000
Essentially, you have wiped out your trading account if the shares of AAPL drop 10%.
This is why I say that leverage can be a double-edged sword.
And you want to use this with responsibility.
If you want to learn more about leverage and how to position size your trade (which is advanced stuff) you can check out the article here.
Pip
A pip stands for Point in Percentage.
For most currency pairs such as the major currency pairs, it is the 4th decimal place.
For example, let’s say EUR/USD is trading at 1.2511
And it moves up by 2 pips.
What this means is that EUR/USD has moved up to 1.2513, but for the JPY currency pairs, it is slightly different.
Let’s say USD/JPY is trading at 120.10 and it drops 5 pips...
Now, USD/JPY is trading at 120.05!
So, bear in mind that pip refers to the smallest price move in the currency pair.
One thing to note is that some brokers also have “pipette.”
And 1 pip is equal to 10 pipettes.
Bid/Ask
The Bid refers to the price that you can sell at.
The Ask refers to the price that you can buy at!
Whenever you are trading Forex or Stocks, it’s not just one price.
It’s always two, the bid and the ask.
For example, EUR/USD is trading at 1.2001/1.2003 (Bid/Ask).
The higher value is always the Ask, and the smallest is always the Bid.
If you want to Long (buy) right now, you would look at the Ask price (1.2003).
If you want to Short (sell) right now, you would look at the Bid price (1.2001).
Spread
The spread is the difference between the Bid and Ask.
Read on…
How to read a Forex chart
Here’s an example of a Forex chart in tradingview:
The red box you see on the lower right (0.66017) is the price right now to trade NZD/USD.
If you want to sell:
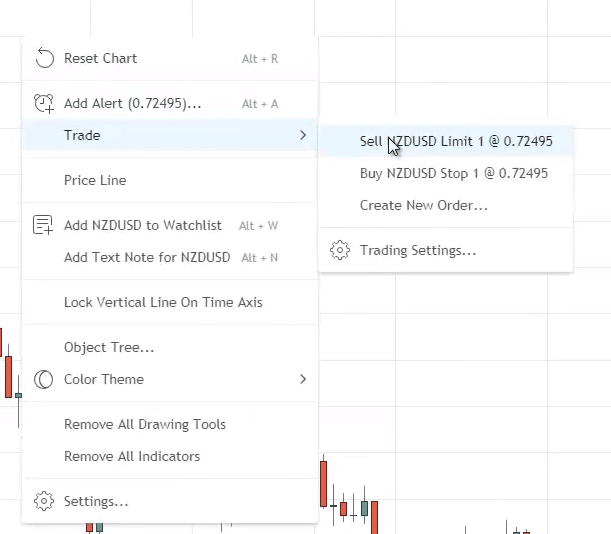
You’ll notice that there are two prices, the bid, and the ask:
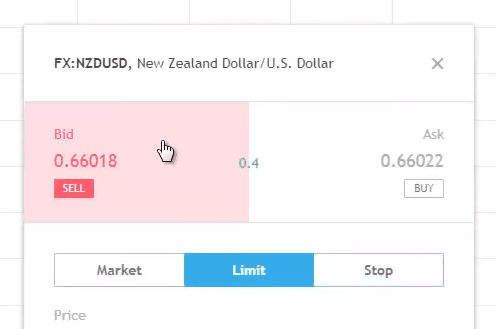
So, if you are to Short, you will sell on the Bid price (0.66018).
And if you are to go Long, you will buy on the Ask price (0.66022).
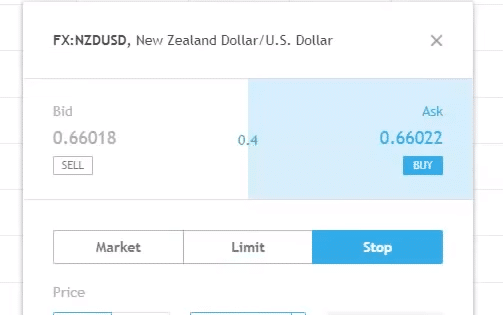
And the difference between the two prices is the Bid-Ask spread (0.4 Pips).
Moving on…
What is a Forex Lot Size
Lot size refers to how much of a Forex currency pair you can buy.
There are different lot sizes:
- Standard lot (100,000 units)
- Mini lot (10,000 units)
- Micro lot (1,000 units)
- Nano lot (Below 1,000 units)
Trading with Nano lot is not offered by all brokers.
Typically brokers that are market makers tend to offer Nano lot sizes for trading.
Otherwise, the most common Forex lot sizes that you’ll trade is either the Standard or Mini Lot.
With that said...
How do you calculate your gain/losses?
How to calculate your gain/losses
Let’s say you went long at 1.2001 in EUR/USD and you sold it at 1.2005, you can tell that you have gained 4 pips.
But how many dollars do you make on this trade?
That depends on the lot you are trading, whether you are trading Standard, Mini, Micro, or Nano lot.
For example…
100,000 units (1 standard lot) is equal to $10 per pip.
One thing to bear in mind is that the value of $10 per pip may vary depending on the currency of your account.
Now…
If you made 4 pips, you will multiply $10 (per pip) and you would have earned $40.
Another example is that if you have a position of 10,000 units (Mini lot) you would have earned $4 ($1 per pip)
So, this is how to calculate your gain/loss trading in Forex.
Next…
The different types of orders
There are a few types of them:
- Market Order
- Limit Order
- Stop Order
- Stop loss Order
Let me explain…
Market Order
It is an order that tells your broker to enter the market right now.
But this order has some Pros and Cons to it.
Pros:
You know for sure you’ll be in the trade.
Cons:
The downside to this is that you are paying a premium, sometimes the market is moving fast up and down.
And if you hit a market order, your trade may not be executed on the price that you desire.
Limit Order
On the other hand, you enter only if the market comes to your desired price level (pullback).
For example, AAPL is trading at $120.
You may tell yourself, “It’s too high, I don’t want to pay $120 for Apple shares!”
What you can do is use a Buy Limit order, and place the order at $100.
This means that if Apple shared comes down to $100, only then will you get filled on the trade!
Pros:
You are entering at a “cheaper” price as you let the market come to your price level.
Cons:
The downside is that you might miss the move, Apple shared may not go back down to $100 and head straight up to $150.
Another downside is that you are trading against the current momentum, you are trading against the down move.
Stop Order
Stop order is typically used when you want to trade a breakout.
Let’s Apple shares right now is $120.
And you notice that the price is not breaking out of the $120 level for the past 2 years.
What you do is that you can place a Buy stop order on Apple shares at $130.
You will only enter the trade if the price hits $130 and above.
Pros:
The pros of this approach are that you are entering your trades with momentum.
Cons:
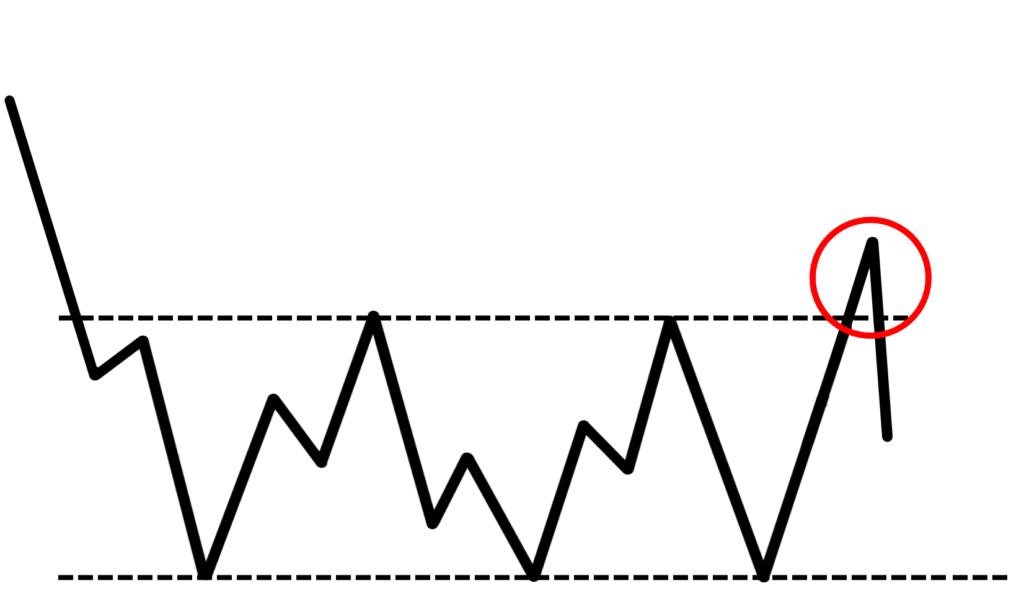
The downside to this is that the move might be a false breakout.
A false break out is when the market is in a range, it breaks out and falls back into the range again:
Stop loss Order
A stop loss order is an order to exit your trade if it goes against you.
It is somewhat like an Insurance to protect your account if the trade goes against you!
Let’s say again that Apple shares are at $100 and you have a stop loss order on $90.
What this means is that if the price goes down to $90, you will automatically exit the trade.
Pros:
The beauty of this is that you are cutting your losses, you’re limiting the damage that could be done into your trading account!
Cons:
Depending on how you set your stop loss, there is a possibility that the market could hit your stop loss and reverse back in your favor.
You might say, “Ah man! Why did I use a stop loss, I’m so silly, now I’m out of the trade and the market went back in my favor.”
Yes, you are going to get that quite a number of times in your trading journey.
It’s part of trading so you want to embrace this fact.
Next...
Different types of Forex chart
Generally, there are many types of Forex charts out there.
But I am just going to share with you three common ones:
- Line chart
- Bar chart
- Candlestick chart
Here’s what they mean…
Line chart
If you look at tradingview, this is a line chart:
This chart connects the closing prices and it shows in the form of a line and you can also change the settings of it:
It’s very useful to identify the direction of the trend if you are not sure.
Bar chart
A bar chart looks something like this:
When looking at a green bar, how you interpret it would be something like this:
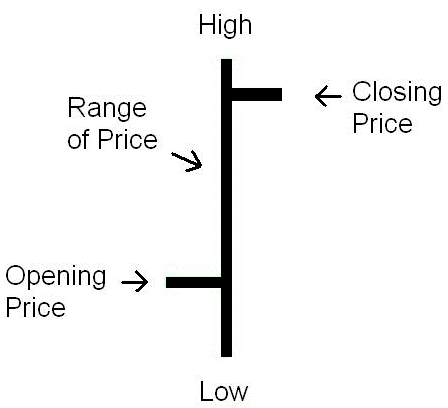
And it is the opposite of the red bar where the opening price is higher and the closing price is lower.
Candlestick chart
The concept is the same as the bar chart:
And this is how you interpret candlestick bars:
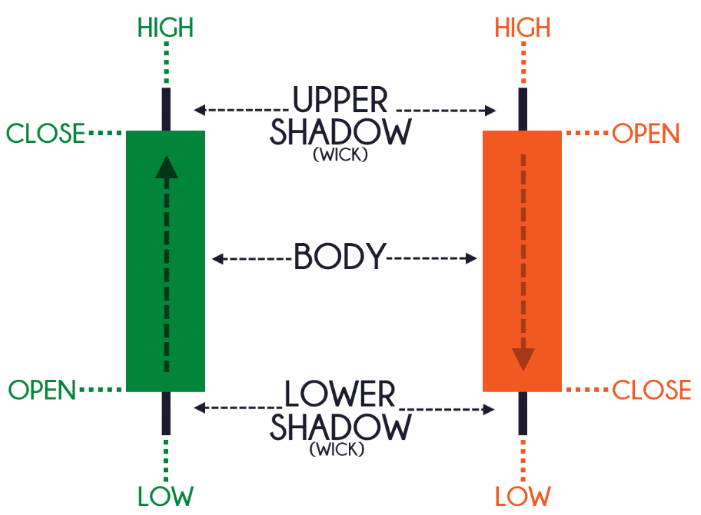
Now that you know how to read the different types of Forex chart.
Let’s move on…
Different types of Forex Analysis
Let’s understand the different types of Forex Analysis!
You have:
- Fundamental Analysis
- Technical Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis
Let me explain…
Fundamental Analysis
Typically, Fundamental analysis deals with:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Interest Rates
- Non-Farm Payroll
These are all the important things to do with Fundamental Analysis.
Technical Analysis
On the other hand, you are using tools like:
- Support & Resistance
- Candlestick patterns
- Fibonacci ratios
- Etc.
Typically, you’ll deal with concepts that deal with charting that boils or falls down under technical analysis.
Sentiment Analysis
As for Sentiment analysis, you are typically trying to gauge the sentiment of the markets.
You are trying to identify what are the players doing.
What you could do is use tools like the…
The commitment of Traders Report
It tells you what are the commercial and speculators are doing.
You also have the…
Long/short ratio
It shows how many traders are long and short.
This gives you sentiment on whether traders are bullish or bearish.
Onwards...
Types of trading strategies
There are many trading strategies out there.
But generally, it can be broken down into these three:
- Position trading
- Swing trading
- Day trading
Here’s what they mean…
Position trading
If you are position trading, you want to capture a trend in the markets.
What you are interested as a position trader is to capture the meat of the trend:
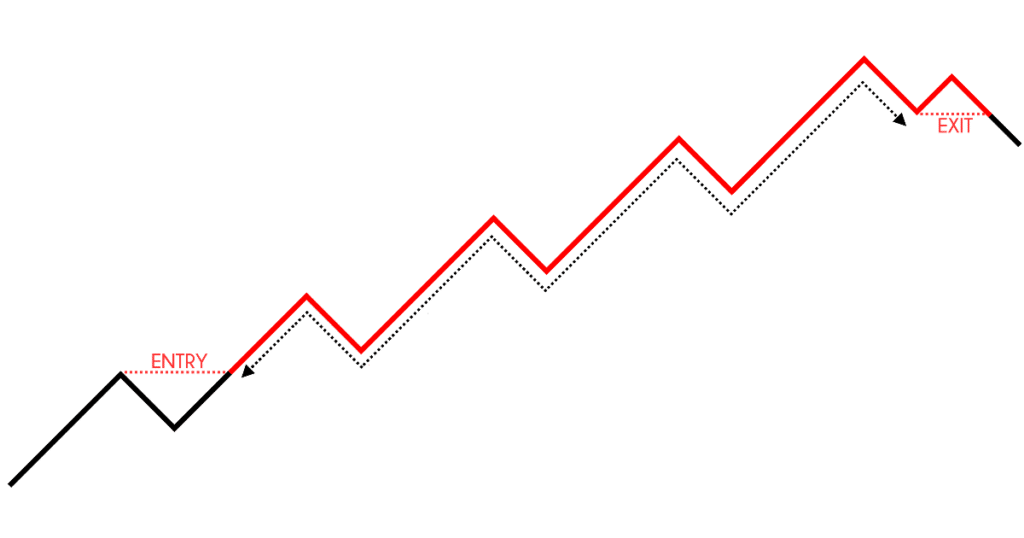
You can get on the lows and the highs.
But you’re just focused on capturing the meat of the trend.
That is what a position would try to do.
You are typically trading the 4-hour timeframe and above.
And this is suited for those with full-time jobs.
Swing trading
On the other hand, you are trading in the 1-hour and 4-hour timeframe.
This is for those with full-time jobs but you want a little bit more action.
Your goal as a swing trader is to capture one swing in the market.
A “swing” in the market looks like this:
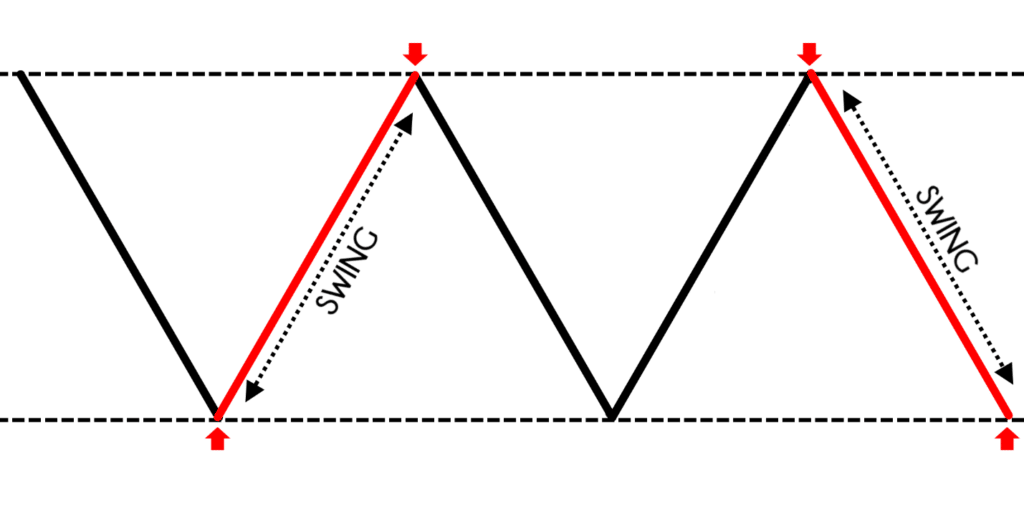
As a swing trader, you are not interested in capturing an entire move but one swing in the market.
Let’s say that the market is in a trend.
What a swing trader would do is to buy near the lows of the pullback:
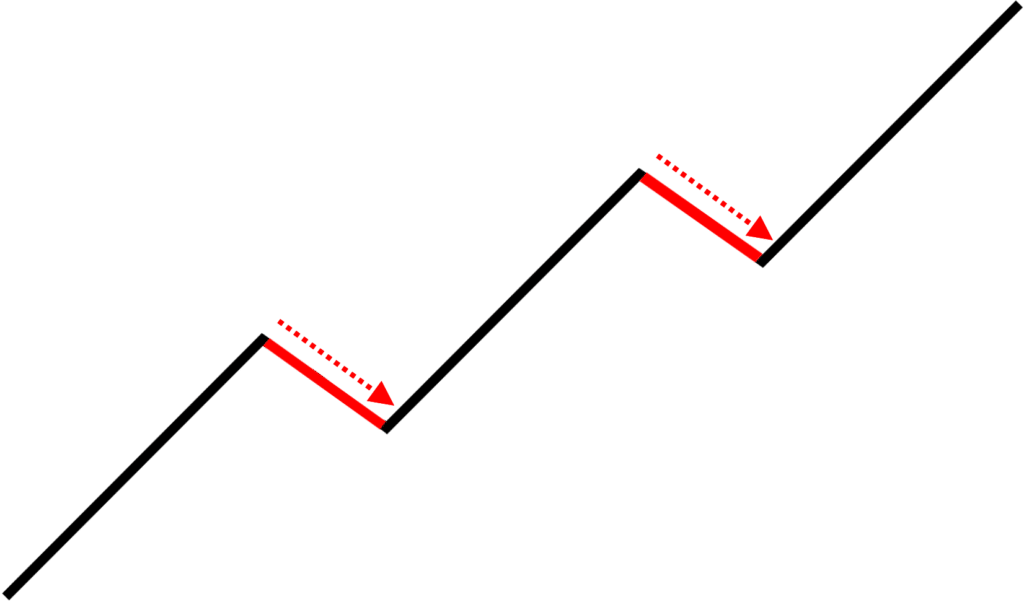
And as the market heads higher, just capture one swing.
Day trading
It is a faster form of trading and you would be trading below the 1-hour timeframe.
This is for those who want to trade for a living.
Day trading is quite hard for those of you who have full-time jobs because day trading requires you to actively watch your positions.
And if you have a full-time commitment elsewhere, day trading is the last thing you want to do.
So, for day traders, you are trading off the lower timeframe and capturing the intraday volatility.
Moving on, let’s talk about…
Different types of Forex brokers
I think this is an important topic, and a topic many of you want to know more about.
Forex brokers can be broken down into these categories:
- Dealing desk broker
- Non-dealing desk broker
First...
Dealing desk broker
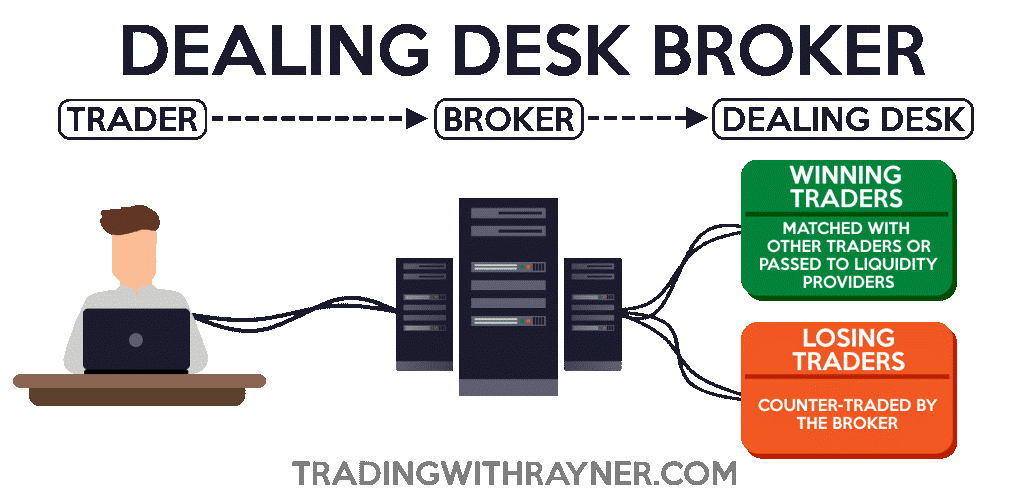
They are brokers that are otherwise called “market maker.”
Some of you might think, “Oh man! Market maker, they hunt your stops!”
Here’s the thing…
There’s nothing wrong about market makers, it’s just the way the business model works.
What it does is that a trader would trade with the broker.
If you are a consistently profitable trader…
The broker will match you with other traders or pass your trades to liquidity providers.
But if you lose consistently, what they would do is trade against your position.
They won’t purposely hunt your stop loss, but they will only take the opposite side of your trade.
Because in the long run, you tend to lose over time.
They won’t go out of the way to purposely stop you out of your trades.
The reason I say this is because the broker industry is highly competitive.
If you’re going to do this to your customers, it’s only a matter of time you will get reported and you might lose your business license altogether.
It’s not worth it just to earn a few measly pips from a few traders to risk losing the entire business operation.
So, here are the following characteristics of a Dealing desk broker:
- Market maker (takes the opposite side of your trades)
- Fixed spread
- Likely to trade nano lots
Non-Dealing desks
A non-dealing desk broker could be of these two:
- Electronic Communications Network (ECN)
- Straight through processing (STP)
With a non-dealing desk broker, what they do is that the trader would trade with the broker, and the broker would directly connect you to the interbank market.
Which means that you could see the order flow with other participants.
An ECN broker would look something like this...
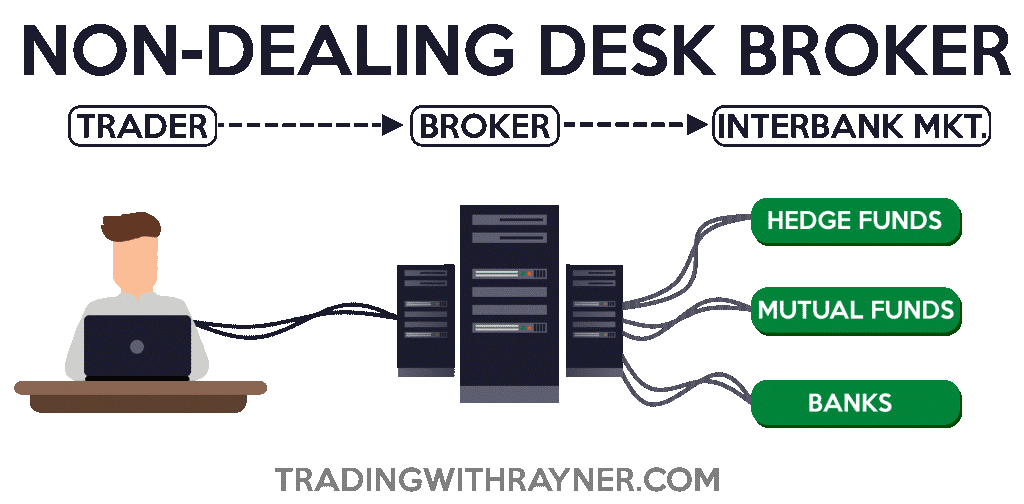
And with Electronic Communication Network you have:
- Direct interaction with liquidity providers and other ECN participants
- You may or may not have to pay for the spread but you will be charged for a commission
Straight through processing looks like this...

What it does is that the broker will give you several prices from all the different liquidity provider and share the most competitive price with you.
They will also mark up the spread slightly and pass on the cost to you.
So, this is how straight through processing broker works:
- Links you with other liquidity providers (Banks, hedge funds, other brokers)
- Variable spreads
This broker is one step behind the ECN broker since you can go directly to the liquidity pool and see the others.
For the STP, you cannot see the orders directly.
Which broker to choose?
For Dealing desk brokers, I would recommend it to:
- New traders
- Swing or position traders
For Non-dealing desk brokers, I would recommend it to:
- Day traders
- Experienced traders
With that said...
How do you select a Forex broker
I’m going to share with you a few things that you want to pay attention to:
- Regulation
- Execution
- Customer service
- Ease of withdrawal
Let’s talk about this…
Regulation
You want to make sure that your broker is regulated and regulated in the right country.
I would suggest that it is regulated by reputable authorities like Monetary Authoritative Singapore (MAS), FCA and a few others from the UK and Australia.
Execution
How are your trades being executed?
Is it instantaneously?
Do you always get a delay or your orders get rejected?
So, you’d want to pay attention to how your broker executes your trade!
Customer service
It is important for a broker to have a live help desk when the market hours are open.
If there is an upcoming news release or you feel like you’ve been stopped out unnecessarily…
You want to speak to a customer service that offers live chat support.
Not when you have to send an email and wait for 3-5 days to get a reply.
Ease of withdrawal
In this day and age, you should get it within 5 working days.
Now, the next part is very important...
How to protect yourself from the broker
Let’s say that you are trading with your broker and find out that they have done something unjust to you.
How can you protect yourself?
Here are a few things you can do:
- Record and screen capture every time you put on a trade or get stopped out
- Share on social media
- Bring up to the authorities
Before you share your issue to social media and authorities…
You would want to reach out to your broker first and ask, “Hey, why is this happening?”
The reason could be because of the news release which widens the spread and liquidity is low.
When liquidity is low, it doesn’t mean that the broker intentionally lowers liquidity to widen the spread.
So, if your stop loss is near the current price before the news release, there’s a good chance that it would get stopped out.
Now…
If you are not happy with your broker’s explanation and you feel that they are doing something fishy behind the scenes…
Share your post in Forex trading groups and let others give you their opinion.
It may get your post viral and hurt your broker’s reputation.
The last thing the broker wants is to have a bad reputation.
But if you still want to do something about it then you would want to bring it up to the authorities.
Let's do a summary of what you've learned...
Summary
- Foreign Exchange (Forex) lets you trade one currency for another
- Participants like Central banks, corporations, banks, and retail traders trade FOREX
- The Forex market has high liquidity, low barriers to entry, better risk management and is open 24/5 of the week
- There are Major Pairs, Crosses, and Exotic Pairs
- The Forex market has a New York session, London session, and Asian session
- The best sessions to trade is the London session and London-New York session overlap
- The best days to trade Forex is from Tuesday to Thursday
- A Forex chart has a Line chart, Bar chart, and Candlestick chart
- Forex Analysis consists of Fundamental and Technical analysis
- The three different types of trading strategies are Position trading, Swing trading, and Day trading
- There are Dealing desk and non-dealing desk brokers
- You should select a Forex broker that has Regulation, easy Execution, good customer Service, and Ease of withdrawal.